| Home > Brazil |
BRAZIL:
Country Profile of Brazil
The magnificent country of Brazil appears to have it all; mountains, lakes, rivers, gorges, world class beaches and of course, the largest part the most famous tropical rainforest in the world; the Amazon, with all its vast biodiversity. It is the fifth largest country in the world and South America’s largest and most influential country with one of the world’s biggest democracies. Brazil is also home the world famous carnival, a huge diversity of cultures, religions, music and cuisine. It is home to both picturesque colonial towns and exciting energetic cities, visited by thousands of international tourists every year. The official language is Portuguese, of which there are various regional accents. In addition, English, Italian, French and German are also spoken, particularly in tourist areas. There is no official religion of Brazil, however, around 70% of the population are Roman Catholic.
|
☻Capital: - Brasilia ☻Area: - Total: 8,547,403 sq km ☻Independence: - 7th September 1822 |
☻Official languages: - Portuguese ☻Population: - 189.6 million (estimated in 2008) |
Geography of Brazil:
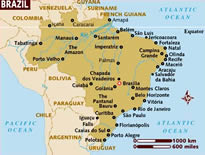 The country covers over 8.5 million sq km and borders all other South American countries with the exception of Chile and Ecuador.Brazil is based on a relatively stable continental crust and as such rarely experiences any volcanic or seismic activities. Over 66% of Brazil’s land surface is covered by the Amazon rainforest, hugely rich in biodiversity. Geographically, Brazil can be roughly separated into three segments. The first is the low lying Amazon basin and the wetlands of the Pantanals, generally speaking, in the north and north-west of the country. The second, the central plateau where Brazil’s capital: Brasilia is located. This is the rugged mountainous area of the south and along the Atlantic coast. The third is the Brazilian Highlands, near Sao Paulo and Rio, the Pico de Neblina can be found in this area: the highest point of Brazil. The country’s population is concentrated in the south-eastern states of Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. The city of São Paulo has a population of over 12 million, while over the city of Rio de Janeiro is home to around 7 million.
The country covers over 8.5 million sq km and borders all other South American countries with the exception of Chile and Ecuador.Brazil is based on a relatively stable continental crust and as such rarely experiences any volcanic or seismic activities. Over 66% of Brazil’s land surface is covered by the Amazon rainforest, hugely rich in biodiversity. Geographically, Brazil can be roughly separated into three segments. The first is the low lying Amazon basin and the wetlands of the Pantanals, generally speaking, in the north and north-west of the country. The second, the central plateau where Brazil’s capital: Brasilia is located. This is the rugged mountainous area of the south and along the Atlantic coast. The third is the Brazilian Highlands, near Sao Paulo and Rio, the Pico de Neblina can be found in this area: the highest point of Brazil. The country’s population is concentrated in the south-eastern states of Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. The city of São Paulo has a population of over 12 million, while over the city of Rio de Janeiro is home to around 7 million.
Education in Brazil:
 The ministry of education, which is controlled by the Brazilian government, is responsible for the country’s educational system and by law, Brazilian children must spend a minimum of 9 years in education. Pre-school education which is available to children under 6 years of age is not mandatory. However from the age of 2, children can attend nursery, kindergarten and pre-school which prepares them in all areas of mental and social development.
The ministry of education, which is controlled by the Brazilian government, is responsible for the country’s educational system and by law, Brazilian children must spend a minimum of 9 years in education. Pre-school education which is available to children under 6 years of age is not mandatory. However from the age of 2, children can attend nursery, kindergarten and pre-school which prepares them in all areas of mental and social development.The mandatory 9 years run from the age of 6 to 14 when children move on to elementary education to study Portuguese,History,Geography, Science, Mathematics, Arts and Physical Education. For the last 4 years the study of one or two foreign languages are also compulsory, these are normally Spanish and English.
Only when students have completed their full elementary education can they advance to an optional 3 year high school education. Students have the option to study Portuguese language, Brazilian and Portuguese literatures, foreign languages; normally Spanish and English, History, Geography, Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry and Biology. In addition, the subjects of Philosophy and Sociology are compulsory.
In order to continue on to higher education, students must have completed the 3 years elementary program and in addition sit an entrance exam. The higher education or undergraduate program is the same as in European countries and can be for either 3 or 4 years depending on the discipline. There is the option of a further year of study in order to gain a professional diploma; the equivalent of a Masters Degree..
Health in Brazil:
 Healthcare in Brazil is the responsibility of the government. Private health care does exist though this is expensive and as such, is out of reach of the majority of inhabitants. All general hospitals and clinics are run by the individual states and vary in standard, many providing inadequate care. Under the Brazilian healthcare system, all persons who are permanent Brazilian residents receive free care with is paid for through the tax system. Limited financial resources are an ongoing problem resulting in a system deprived of up to date technology, medical research and adequate staff training. A survey carried out in 2008 revealed that life expectancy in males was at 72 years and 76 years for females, this is somewhat lower that European and Eastern countries. However, a recent primary care program which has been set up between Brazil and the United Kingdom is helping to increase knowledge through training. As a result, it is forecast that life expectancy will rise over the next 2 decades as a result of improvements in medicine and a wider availability of vaccines. Due to the sheer size of the country however, malnutrition remains a severe problem in the northern states, where almost half of all families live in extreme poverty with insufficient good quality food. Malnutrition therefore, amongst the next generation is a constant problem and burden on an already over-stretched healthcare system.
Healthcare in Brazil is the responsibility of the government. Private health care does exist though this is expensive and as such, is out of reach of the majority of inhabitants. All general hospitals and clinics are run by the individual states and vary in standard, many providing inadequate care. Under the Brazilian healthcare system, all persons who are permanent Brazilian residents receive free care with is paid for through the tax system. Limited financial resources are an ongoing problem resulting in a system deprived of up to date technology, medical research and adequate staff training. A survey carried out in 2008 revealed that life expectancy in males was at 72 years and 76 years for females, this is somewhat lower that European and Eastern countries. However, a recent primary care program which has been set up between Brazil and the United Kingdom is helping to increase knowledge through training. As a result, it is forecast that life expectancy will rise over the next 2 decades as a result of improvements in medicine and a wider availability of vaccines. Due to the sheer size of the country however, malnutrition remains a severe problem in the northern states, where almost half of all families live in extreme poverty with insufficient good quality food. Malnutrition therefore, amongst the next generation is a constant problem and burden on an already over-stretched healthcare system.Politics in Brazil:
 Brazil experienced decades of military dictatorship between the mid-sixties and mid-eighties. During this time, the military exercised total control over the economy, politics, popular media and all systems of communication. Throughout this period, many leftist politicians were arrested and exiled. However, as a result of a severe recession in 1985, peaceful protests, followed by elections, led to the formation of a democratic government and the military lost power and influence. Three years later, the Brazilian Constitution was created in 1988 which now supports a democratic government. For all literate persons between the ages of 18 and 69, voting in Brazil is compulsory. In addition, for those who are 16 and 17 years old, or those who are 70 and over, voting is optional. The executive, legislative, and judicial branches make up the government, over which the president exercises ultimate power. The president is elected by ballot and once he takes up position, serves a 4 year term of office. Over half of government revenue comes from personal taxes with a maximum rate being set at 25%. A value added tax on goods and services ranges from 10-15%.
Brazil experienced decades of military dictatorship between the mid-sixties and mid-eighties. During this time, the military exercised total control over the economy, politics, popular media and all systems of communication. Throughout this period, many leftist politicians were arrested and exiled. However, as a result of a severe recession in 1985, peaceful protests, followed by elections, led to the formation of a democratic government and the military lost power and influence. Three years later, the Brazilian Constitution was created in 1988 which now supports a democratic government. For all literate persons between the ages of 18 and 69, voting in Brazil is compulsory. In addition, for those who are 16 and 17 years old, or those who are 70 and over, voting is optional. The executive, legislative, and judicial branches make up the government, over which the president exercises ultimate power. The president is elected by ballot and once he takes up position, serves a 4 year term of office. Over half of government revenue comes from personal taxes with a maximum rate being set at 25%. A value added tax on goods and services ranges from 10-15%.